Anti-Acne Ingredients: A Complete Dermatologist Guide
April 21, 2025 2025-04-21 10:17Anti-Acne Ingredients: A Complete Dermatologist Guide
As an Amazon associate, Dermatocare earns from valid purchase made by clicking on the affiliate links in this blog.
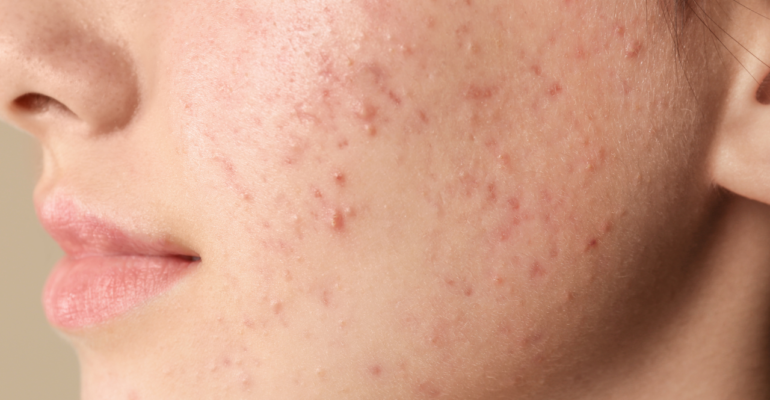
Anti-Acne Ingredients: A Complete Dermatologist Guide
Introduction
Acne is a multifactorial skin condition involving excess oil production, clogged pores, inflammation, and bacterial overgrowth. A wide array of active ingredients, both pharmaceutical and botanical, are available to target different stages of acne. This comprehensive guide categorizes anti-acne ingredients based on their mechanism, suitability for acne type, usage, and safety profile.
Key Anti-Acne Ingredients and Their Benefits
- Benzoyl Peroxide
- Benefits: Kills acne-causing bacteria (C. acnes), reduces inflammation, and helps prevent clogged pores.
- Best For: Inflammatory acne like red pimples, pustules, cysts.
- Salicylic Acid (BHA)
- Benefits: Exfoliates inside pores, reducing blackheads and whiteheads.
- Best For: Comedonal acne like black/whiteheads
- Retinol / Retinoids (Adapalene, Tretinoin)
- Benefits: Promote cell turnover, unclog pores, and reduce post-acne marks.
- Best For: All acne types, especially persistent or scarring acne.
- Azelaic Acid
- Benefits: Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, reduces pigmentation.
- Best For: Sensitive, acne-prone skin with pigmentation in form of brown scars.
- Niacinamide
- Benefits: Anti-inflammatory, sebum-regulating, strengthens the skin barrier.
- Best For: Mild acne and maintenance phase.
- Glycolic Acid (AHA)
- Benefits: Surface exfoliation, brightens skin, helps with post-acne marks.
- Best For: Comedonal acne with dullness or hyperpigmentation.
- Clindamycin
- Benefits: Topical antibiotic targeting C. acnes.
- Best For: Inflammatory acne; used in short-term combination therapy.
How to Use Anti-Acne Ingredients
- Start gradually: Introduce one active at a time, especially retinoids and acids.
- Day vs. Night: Benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and niacinamide can be used day or night. Retinoids should be used at night.
- Layer wisely: Avoid combining two group actives at once; use a minimalist approach and focus on hydration.
- Sun protection: Essential when using exfoliants, retinoids, or azelaic acid.
Matching Ingredients to Acne Type
| Acne Type | Best Ingredients |
|---|---|
| Comedonal Acne | Salicylic acid, glycolic acid, retinoids |
| Inflammatory | Benzoyl peroxide, clindamycin, niacinamide, retinoids |
| Hormonal Acne | Retinoids, niacinamide, azelaic acid |
| Acne with PIH (brown marks) | Azelaic acid, glycolic acid, retinoids, niacinamide |
| Sensitive Skin | Azelaic acid, niacinamide, low-dose salicylic acid |
Herbal Anti-Acne Ingredients
| Ingredient | Use/Benefits |
| Achyranthes aspera | Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial |
| Onion (Allium cepa) | Helps in reducing scars and inflammation |
| Neem | Antibacterial, astringent, sebum-regulating |
| Hemp | Anti-inflammatory, calms skin, regulates sebum |
| Echinacea | Reduces inflammation, promotes healing |
| Rosemary | Antioxidant, antimicrobial |
| Tea Tree Oil | Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory |
| Eucalyptus | Antiseptic, decongests clogged pores |
| Aloe Vera | Soothing, hydrates, supports healing |
| Turmeric (Curcuma longa) | Antibacterial, reduces redness and pigmentation |
| Green Tea | Rich in EGCG; reduces sebum, inflammation |
| Guggul | Hormonal balancing; traditionally used in Ayurveda |
| Sea Buckthorn | Anti-inflammatory, heals and soothes skin |
| Vitex negundo | Used in Ayurvedic medicine for hormonal acne |
| Andrographis paniculata | Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties |
| Salmalia malabarica | Astringent and soothing properties |
Side Effects
- Common: Redness, dryness, irritation, purging.
- Rare: Allergic contact dermatitis (especially from botanicals or essential oils).
- Prevention: Patch test new products, moisturize adequately, use actives as directed.
Who Should Avoid Anti-Acne Ingredients?
- Pregnant or lactating women: Avoid retinoids and certain essential oils.
- Individuals with eczema or rosacea: Avoid high-strength acids and benzoyl peroxide.
- Allergy-prone skin: Use caution with herbal extracts and essential oils.
Conclusion
Successful acne treatment hinges on choosing the right ingredients based on acne type and skin sensitivity. A dermatologist-guided approach ensures efficacy while minimizing side effects. While pharmaceutical actives remain the gold standard, many botanical ingredients offer complementary benefits and may enhance outcomes when used judiciously. Always prioritize gentle, consistent care over aggressive multi-active regimens.
ROUTINE FINDER
Get free dermatologist-recommended regime by choosing your skin or concerns.

FACE

HAIRS

CHILD

BODY




