Stubborn Dandruff: Is It Seborrheic Dermatitis or Scalp Psoriasis?
April 23, 2025 2025-04-23 11:32Stubborn Dandruff: Is It Seborrheic Dermatitis or Scalp Psoriasis?
As an Amazon associate, Dermatocare earns from valid purchase made by clicking on the affiliate links in this blog.
Stubborn Dandruff: Is It Seborrheic Dermatitis or Scalp Psoriasis?
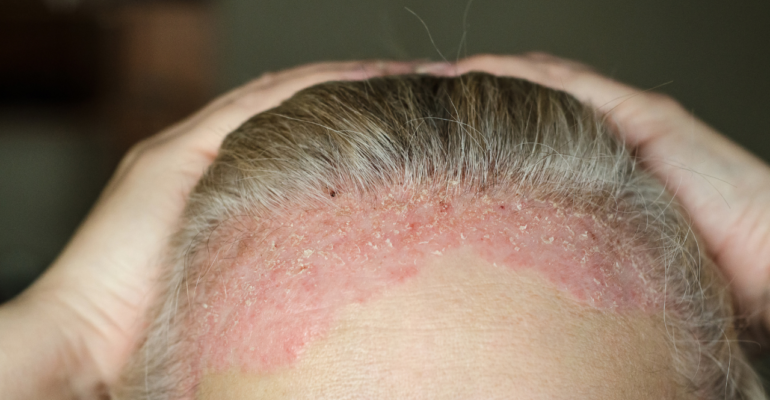
If your dandruff persists despite using anti-dandruff shampoos, it may not be simple dandruff at all. Two common dermatological conditions—seborrheic dermatitis and scalp psoriasis—can closely mimic dandruff, making it difficult to differentiate without expert guidance. While both conditions involve flaking and itching, their underlying causes, clinical features, and treatments differ significantly.
Identifying the correct diagnosis is crucial to selecting the right treatment and achieving long-term relief. This article offers a clear differentiation between seborrheic dermatitis and scalp psoriasis, including their key features, a comparison table, and appropriate treatment options.
Features of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory condition primarily triggered by an overgrowth of the yeast Malassezia that thrives on oily skin. It commonly affects areas rich in sebaceous (oil) glands.
Key Characteristics:
- Greasy, yellowish-white flakes that often adhere to the scalp.
- Mild to moderate itching and occasional burning sensation.
- Redness or pinkish patches, especially around the scalp, eyebrows, nasolabial folds, and behind ears.
- Worsens with stress, cold weather, and lack of scalp hygiene.
- Responsive to anti-fungal shampoos and topical corticosteroids.
Features of Scalp Psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis is an autoimmune skin disorder characterized by an overproduction of skin cells, leading to thick, scaly plaques.
Key Characteristics:
- Thick, silvery-white scales that form raised plaques.
- Severe itching, sometimes accompanied by soreness or bleeding if scratched.
- Clearly demarcated plaques with sharp borders.
- May extend beyond the scalp, affecting the neck, forehead, or ears.
- Often seen in individuals with psoriasis elsewhere on the body (e.g., elbows, knees).
- Less responsive to anti-dandruff shampoos; requires immunomodulating treatments.
Comparison Table: Seborrheic Dermatitis vs. Scalp Psoriasis
| Feature | Seborrheic Dermatitis | Scalp Psoriasis |
|---|---|---|
| Flake Appearance | Greasy, yellowish, thin flakes | Thick, dry, silvery-white scales |
| Itching | Mild to moderate | Moderate to severe |
| Skin Appearance | Pink or red with greasy patches | Bright red plaques with clearly defined edges |
| Plaque Borders | Ill-defined | Well-demarcated |
| Common Areas Affected | Scalp, eyebrows, nose folds, behind ears | Scalp, neck, forehead, elbow, knees, other body areas |
| Associated Conditions | Oily skin, dandruff | Psoriasis on elbows, knees, nails |
| Response to Anti-dandruff Shampoo | Good response to antifungal shampoo | Minimal response, requires psoriasis treatment |
| Chronicity | May relapse but manageable | Chronic and may require long-term therapy |
Treatment Options
1. Seborrheic Dermatitis Treatment
- Shampoos containing anti-fungal agents Ketoconazole (2%), luliconazole tec.
- Topical Treatments:
- Corticosteroids and antifungal combinations
- Calcineurin inhibitors (e.g., pimecrolimus, tacrolimus) for sensitive areas
- Maintenance: Use medicated shampoo once weekly after control. Sometimes, topical treatment twice a week is needed in stubborn cases.
- Lifestyle Tips: Reduce stress, avoid harsh hair products, maintain good scalp hygiene.
2. Scalp Psoriasis Treatment
- Topical Treatments:
- Corticosteroids (betamethasone, clobetasol)
- Calcipotriol (Vitamin D analog)
- Coal tar or salicylic acid for scale removal
- Shampoos:
- Coal tar shampoos
- Salicylic acid-based shampoos
- Systemic/Advanced Therapies (for severe or resistant cases):
- Methotrexate, cyclosporine
- Biologics (e.g., secukinumab, ustekinumab)
- Phototherapy: UVB light therapy may be helpful in some cases.
Conclusion
Stubborn dandruff could be an indication of an underlying condition like seborrheic dermatitis or scalp psoriasis. While they may look similar at first glance, their differences in scaling pattern, extent, and treatment response are key to accurate diagnosis. Misidentifying one for the other can delay effective treatment and worsen the condition.
If over-the-counter remedies fail or if you notice thick plaques, severe itching, or involvement beyond the scalp, it’s time to consult a dermatologist.
For a personalized scalp care routine, use the Dermatocare Regime Finder Tool. It offers dermatologist-curated regimens for concerns like stubborn dandruff, scalp psoriasis, hair fall, and premature greying, helping you manage scalp conditions holistically and effectively.
ROUTINE FINDER
Get free dermatologist-recommended regime by choosing your skin or concerns.

FACE

HAIRS

CHILD

BODY




